In business, debt-to-income (DTI) ratio is one aspect of your financial health that lenders evaluate to determine how much debt you can handle. Find out more about DTI, including how to calculate debt-to-income ratio, why it’s important and how you can improve yours.
What Is Debt-to-Income Ratio?
Your DTI ratio is expressed as a percentage and indicates how effectively you manage your company’s debts and spend money on a monthly basis. For instance, if your debt-to-income ratio is 25%, that means 25% of your gross income each month is dedicated to debt repayment. As such, the lower the percentage, the better (and the easier it should be for your business to qualify for financing if you should need it).
How to Calculate Your Debt-to-Income Ratio
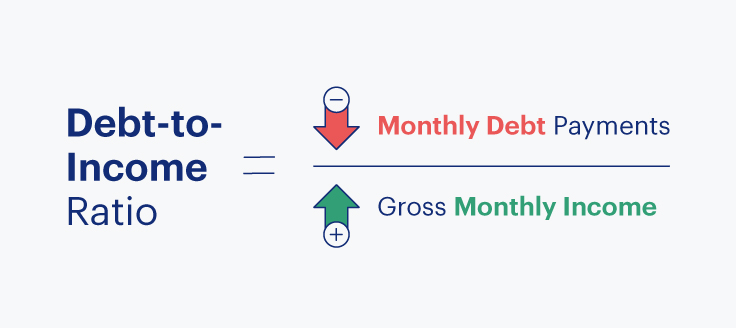
DTI is calculated by dividing your monthly debt payments by your monthly gross income as you can see in the following debt-to-income ratio formula:
If you prefer, you can calculate your ratio by using a debt-to-income calculator, such as Bankrate’s tool.
Whether you choose to calculate your DTI ratio manually or digitally, be certain you’re working with complete data to ensure your ratio is accurate.
Monthly Debt Payments
Your total monthly debt payments cover any installment of a debt obligation. When calculating your small business debt-to-income ratio, lenders will usually review both personal and business debts.
These debt payments typically include:
- Minimum business credit-card payments
- Mortgage
- Personal and car loan installments
- Real-estate taxes
- Homeowner’s insurance
If you use your business accounts to pay off student loans, expect lenders to include those payments in your business DTI.
Monthly subscriptions and similar expenses that can be terminated at any time aren’t included in your total monthly debt payments. Variable regular expenses, such as utilities and gas, are excluded too.
Similar to your debt service coverage ratio, lenders will calculate your monthly debt payments using your existing debts and prospective loan payment.
Gross Monthly Income
Your gross monthly income is the total amount of income you earn in one month before taxes and other deductions. To estimate your gross monthly income, take your annual gross income and divide by 12.
-
Total Gross Monthly Income = Annual Income ÷ 12
It’s important to note that lenders will usually only consider non-W2 earnings if you’re able to provide your 2 most recent federal tax returns showing proof of income over those taxable years.
What Is a Good Debt-to-Income Ratio?
Generally, a good DTI ratio is anything at or below 36%. This ideal debt-to-income ratio indicates to lenders that you’re more likely to make your scheduled loan payment each month.
There are 3 primary DTI ratio benchmarks you need to be aware of:
| Debt-to-Income Ratio | Detail |
| 36% and Under (Good) | This is a healthy DTI ratio. Your debt, compared with your income, is manageable. In this range, your likelihood of approval is good. |
| 36% – 49% (Okay) | In this range, lenders see room for improvement, but it could be enough to secure a loan. |
| 50% and Higher (Poor) | With more than half of your income going toward debt payments, it will be difficult to save money or deal with unexpected expenses. Securing a loan will be challenging. |
While these DTI ratio standards are commonly accepted, lenders will have their own standards depending on the type of financing you need.
For example, some lenders won’t offer a business loan if a company’s DTI is higher than 43%. Other lenders focus on calculating DTI without mortgage or rent payments, meaning they’re looking for a ratio that excludes those major payments but would still come in at or under 25%.
DTI Calculation Example
Say your gross monthly income is $8,000 and you have a current monthly debt payment of $750. Given the information, your current debt-to-income ratio is calculated as follows:
$750 ÷ $8,000 = 9.375% DTI
You’re looking to apply for a $50,000 loan with a new lender, with an amortized monthly payment of $1,500. As part of the assessment process, the lender will estimate your new debt-to-income ratio by adding the anticipated $1,500 debt payment to your current $750 debt payment:
($750 + $1,500) ÷ $8,000 = 28.125% DTI
With a DTI of slightly more than 28%, you would more than likely be approved for the $50,000 loan in this example.