Many digital marketers consider competitor websites to be their only enemy, but search engines themselves can stand in your way of receiving more organic traffic.
It’s important to “know your enemy” and understand how search engines work so you can put together a search engine optimization (SEO) and content plan that maximizes results.
What Is the Goal of a Search Engine?
The main goal of any search engine is to generate and retain users. Essentially, Google, Bing and others want people to like the service and continue to use it so they can make money off of advertising. More users equal more money they can charge for pay-per-click (PPC) campaigns and other channels.
Because of this, they need to give users the best possible experience. This includes good user experience (UX) and a friendly user interface (UI) but, most importantly, they need to provide great search results.
So they use proprietary algorithms to scour the internet and find valuable, informational content that makes users trust the search engine and return the next time they’re seeking answers.
How Do Search Engines Work?
Search engines work by crawling through websites, following links to discover new pages and documenting the content to create an index that they can pass through their algorithms and serve their users.
They do this through 3 functions:
- Crawling: Using bots to crawl the code and content of pages all over the internet.
- Indexing: Placing the pages they find in an index that can be stored and displayed as a result on search-engine results pages (SERPs).
- Ranking: Determining the best results to provide a user with on a case-by-case basis and placing them in order from most to least relevant.
What crawlers find and index determines what page is ranked on top of SERPs, which brings in traffic to a site.
Crawling: How Search Engines Find Your Pages
Search-engine crawlers (commonly called bots or spiders) flow from page to page through links, finding and documenting a page’s existence and content. This is the first step search engines take to find content to provide its users.
If a bot doesn’t crawl across your page, you won’t have a chance of ranking and reaping the benefits of SEO.
How Search Crawlers Work
The first thing search engine crawlers do is download a website’s robots.txt file. A robots.txt file is located in the root directory of your site (for example yoursite.com/robots.txt). It suggests to crawlers and bots what pages should and shouldn’t be crawled on a site, as well as how fast they should be crawled.
Search engines use varying algorithms and rules to determine how often and how many pages should be crawled for a website. For example, an older site that updates content daily will be crawled more frequently than a new site that is mostly untouched weekly.
When crawling through a page, bots look at the source code and content to determine what a page is all about. They download internal links to other pages on the site, which they use to move on and crawl those pages.
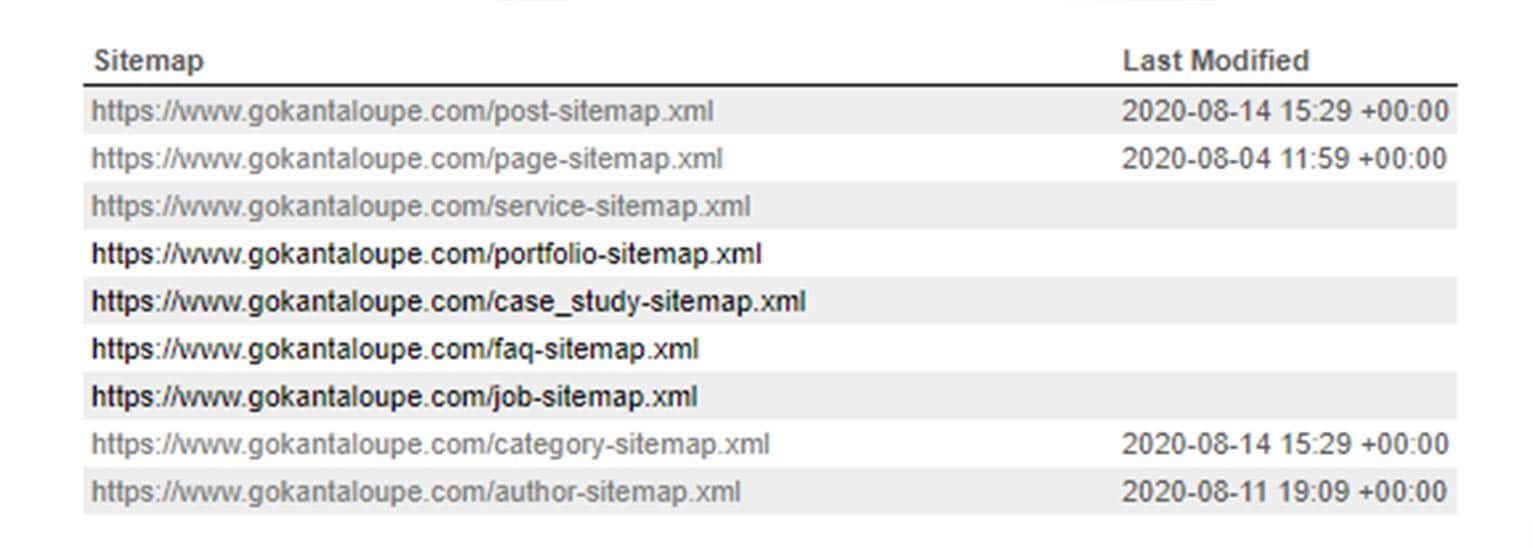
Sitemaps
Sitemaps allow websites to deliver sets of uniform resource locators (URLs) to search engines. This lets crawlers find pages that may be hidden deep in a site.
You can set your sitemap up to categorize each type of content on your site such as blogs, product pages and frequently asked questions.
Unlike robots.txt files which just give directives on what should and shouldn’t be crawled, sitemaps let you tell search engines exactly what URLs are important to your site and should be indexed.
How to Make Sure Your Pages Are Crawled
Optimizing the core pieces of your site’s technical SEO will ensure that important pages on your site are crawled by search engines.
Robots.txt
Your first step is to go into your robots.txt file. Make sure your robots file isn’t blocking Googlebot and other important crawlers from accessing your pages.
It’s a good idea, however, to disallow them from viewing pages you don’t want on SERPs. This can include site search pages and those created by third-party software, among others.
Sitemaps
Go through your sitemap and remove any unwanted URLs. This includes 4XX pages, 5XX pages, 302 redirects, URLs that lead to a 301 redirect and anything else that you don’t want showing up on SERPs.
Site Architecture
Use internal links to make it easier for crawlers to find your page. Make sure each page on your site has a link going to it from another, whether it be through navigation or a related page.
It’s important to limit the number of clicks it takes to get to an important page on your site. Generally, you don’t want any pages to take more than 3 clicks to be reached.
Indexing: How Search Engines Categorize and Store Pages
After crawling a page, search engines add it to its expansive index of pages across the internet. However, it isn’t a given that your page will be added. It’s important to understand what goes into indexing in SEO.
What Is Search-Engine Indexing?
Search-engine indexing is the process of storing and categorizing a web page after it has been crawled and analyzed. Based on what the crawlers find in the content of the page, it’s rendered and placed in a database, ready to be served to users.
When a page is added to this index, it can easily be read by the search engine’s algorithm to determine whether the page is relevant to a user on a case-by-case basis. Traits such as freshness, keyword relevance and more are taken into consideration.
Without the index, search engines would have to crawl pages every time a user enters a search query. As you can imagine, this would exponentially increase how long it takes to get an answer to your question, gobbling up computing power even giants such as Google couldn’t afford.
How to Get Search Engines to Index Your Site
Unsurprisingly, many site owners ask how to get Google to index their site. Fortunately, it’s as easy as following the basic best practices of technical SEO.
If your site is already established and is regularly crawled, odds are search engines aren’t having difficulty indexing your pages. Depending on your site, crawlers could index your site as many as a few times a week to a few times a month, indexing new pages as they find them.
Getting a New Site Indexed
For new sites, you may have to manually submit your sitemap or individual URLs to let crawlers know your site is there. From there, they’ll determine how to index your pages and crawl your site based on its value and how often you update it.
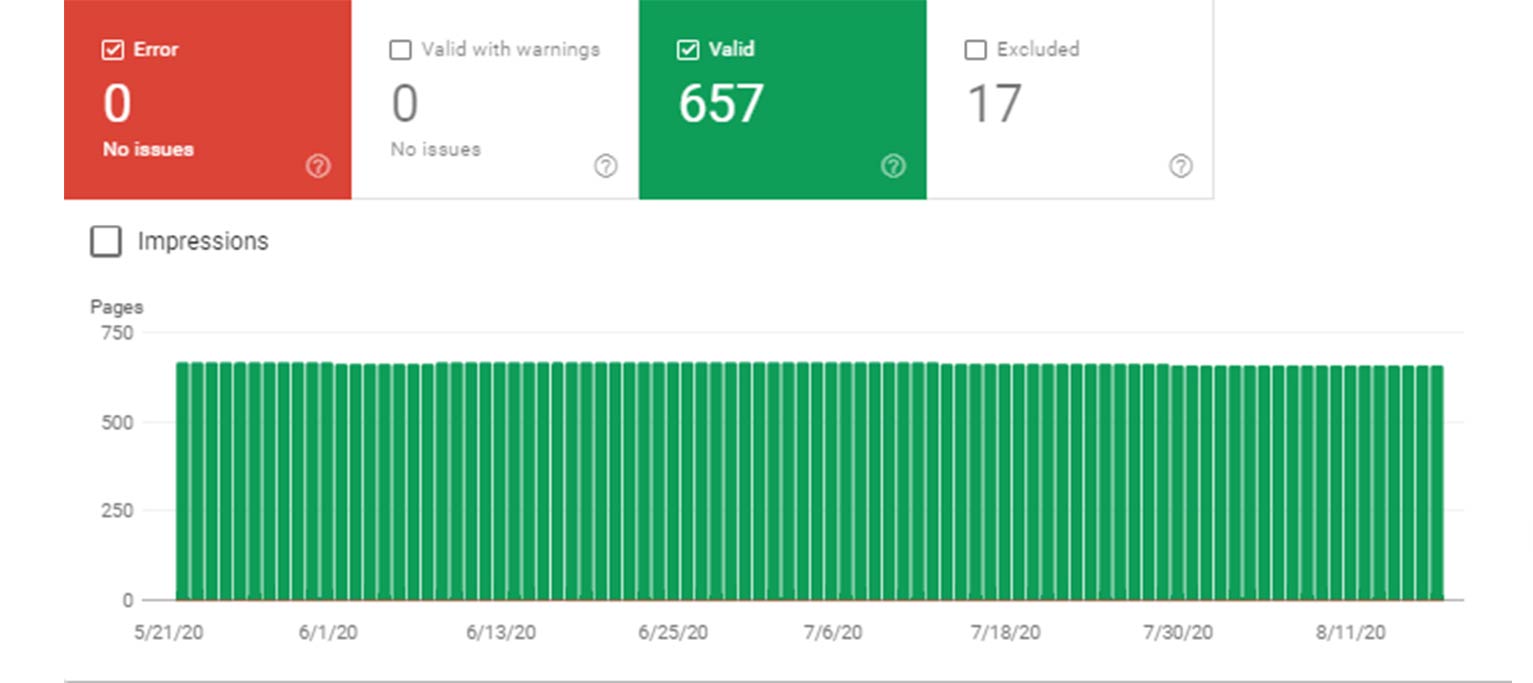
You can check which pages on your site are indexed by Google in Search Console“Coverage” report. There, you’ll see a list of URLs in Google’s index, plus any pages that have outstanding errors keeping them from being indexed. The “Excluded” section shows new pages and others that have been crawled but not placed in the index.
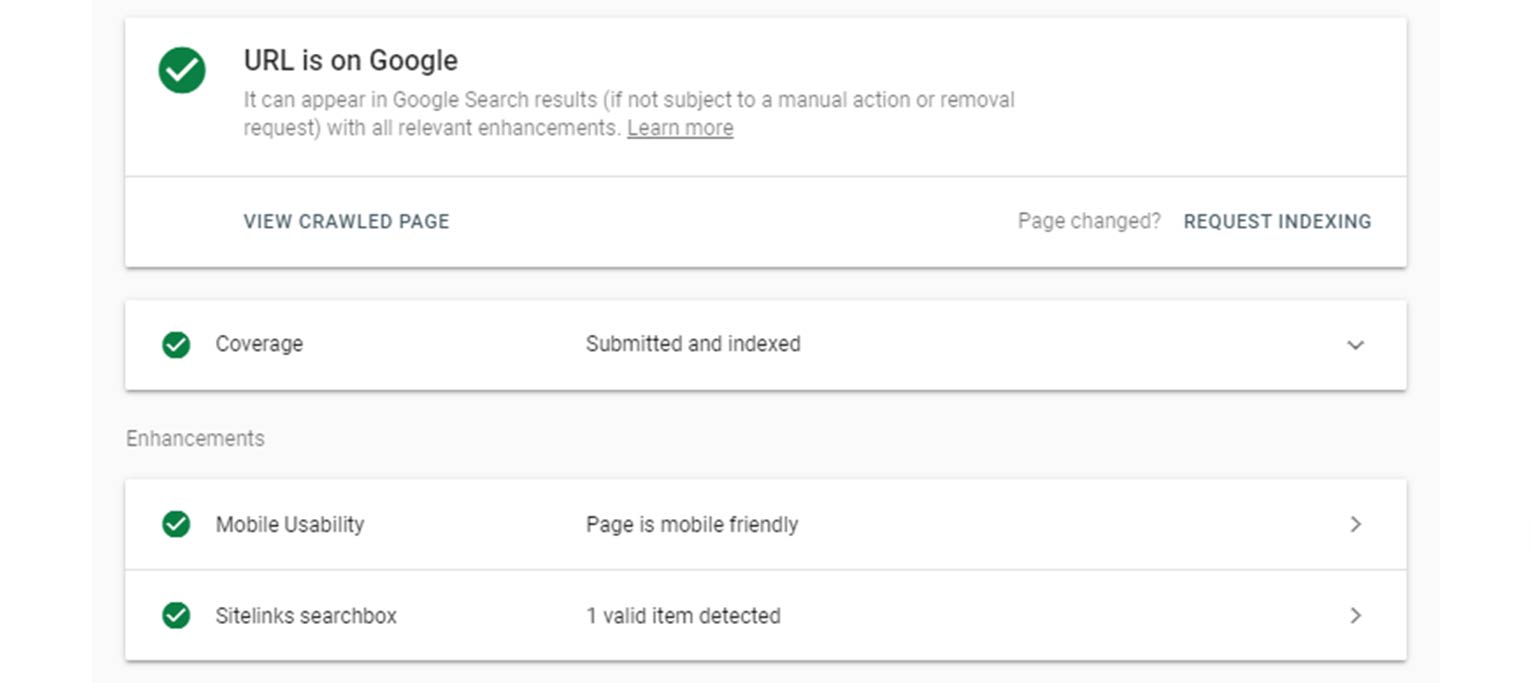
You can also use the URL inspection tool in Search Console to check on individual URLs. This tool allows you to see if a specific page — maybe one that you just posted that is time-sensitive — has been indexed yet.
If it hasn’t, or you’d like Google to index an updated version of it, you can request that they re-crawl and index the current version of the URL.
Reasons Why a Page Isn’t Indexed
If a search engine isn’t indexing your pages, it’s likely because it hasn’t seen them. Search engines index pages when they crawl them, and many new sites or those that aren’t updated often don’t get crawled as frequently, saving bot effort for what they deem to be more important sites/pages.
However, there are a few other reasons why a search engine wouldn’t index a page.
- The site has a “noindex” tag in the <head> of the page’s code.</head>
- Internal links on (or pointing to) the page are labeled “nofollow.”
- The content is the same as another and not properly canonicalized.
By running a site audit or staying on top of your site’s technical SEO, you can ensure that nothing stands in the way of having your most important pages added to a search engine’s index when it’s crawled.
How Do Search Engines Rank Results?
Search engines rank results by taking what they found by crawling and indexing pages and delivering the most relevant results to users based on proprietary algorithms.
They all work similarly, but we’ll use the algorithm of the most popular search engine, Google, as an example.
How Does Google’s Algorithm Work?
Google’s algorithm aims to match a specific search query to the most relevant pages available in their index.
The algorithm is very complex and isn’t very transparent. Since it’s proprietary and Google makes money by having an algorithm that produces better results than its competitors, we don’t know 100% what it takes to get top rankings.
This leads to misinformation and bad advice from SEO “experts” who claim to know how to beat the system. (They don’t.)
There’s nobody outside of the people who work on the algorithm that knows exactly what factors go into Google search rankings and how important each is.
We do, however, have a good idea of what they are.
Search Engine Ranking Factors
Hundreds of SEO ranking factors go into how Google and other search engines choose which page is the best to give a specific user. Some are much more important than others but, again, there’s no concrete guide for SEO.
Some of the most important factors to consider include:
- How relevant the content is to the query and the user
- Content value
- Page loading speed and user experience (UX)
- Page titles, headers and keyword inclusion
- Authoritative links (internal and external)
How much each factor matters to rankings is very fluid. Search engines frequently update their algorithms, making adjustments throughout the year to better serve their users. Many of these include small tweaks to what ranking factors are weighed most heavily, but about once a year or so there are larger updates that can change the way SEO campaigns are strategized.
How Search-Engine Algorithms Rank Results
By rating all of the pages in their index by these ranking factors, search engines rank results that will lead to the best experience for their users. Understanding how some of these ranking factors work will help you maximize your SEO campaign’s effectiveness.
Relevance and Search Intent
As Google and other search engines strive to provide the best results for their users, your page’s relevance to the topic has become arguably the most important ranking factor.
Google’s machine learning algorithms find out what a user wants based on their query, previous behavior and more. Then, they match that up with the most relevant pages from their index. Advances in Natural Language Processing (NLP)research allow Google to better understand small differences in syntax that can get the right result for users who want something specific but use an ambiguous query.
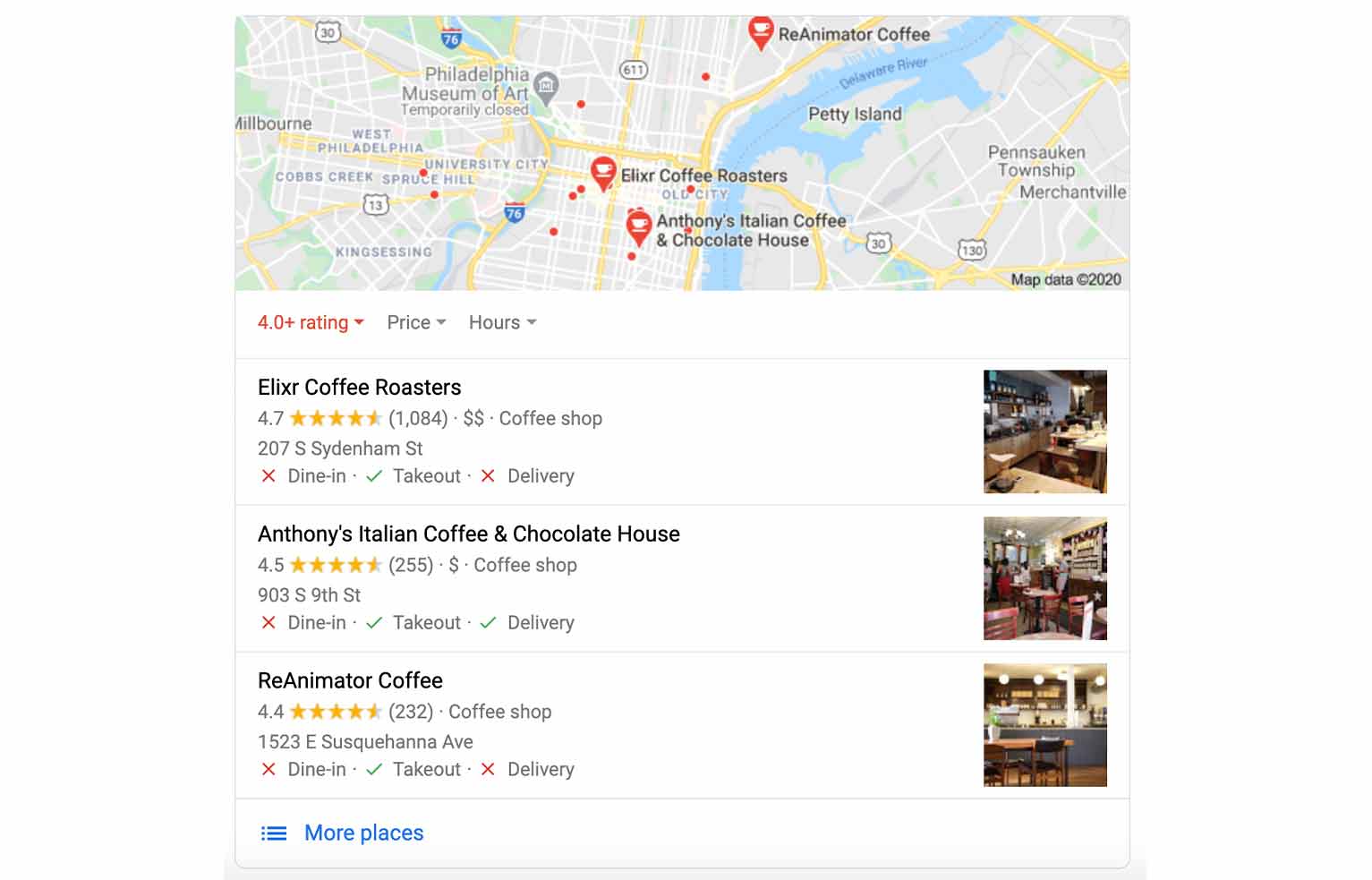
Take this simple example: A user who searches for “best coffee shop” probably isn’t looking for the best place to get a coffee across the globe. Google understands this and will provide local results.
Here’s the thing: Google has gotten very good at matching user intent to relevant pages, even those much more ambiguous than this example.
That makes it critical to research what pages ranking for a certain keyword are all about before creating your own page. If not, you could be wasting time composing a page that has no chance to rank for the keyword you may think is valuable to you.
Content Value
Content is king. Not only does it have to match the intent of the user, but it must also go above and beyond to make sure that the user is happy they found it.
Search engines reward content that is accurate and updated. Indeed, a page that goes more in-depth and covers everything search engines believe the user wants will be given precedence.
Remember, user happiness is the most important thing to consider. Making sure a page offers the most value to users keeps them (and search engines) happy, which leads to high rankings.
Page Loading Speed and UX
Page speed and UX are becoming increasingly important to how search engines rank pages. Google is even planning a huge algorithm update for 2021 that will put a bigger focus on these factors.
That’s right: The update is so important that the often-opaque Google has announced it months in advance.
Factors such as how quickly a page becomes interactive, the presence of obstructive interstitials, mobile SEO and more are big parts of making a great user experience. Keying in on those metrics helps search engines rank and serve users with results that keep them coming back.
Titles, Headers and Keywords
No, it isn’t 2010 anymore when it was possible to rank by stuffing keywords into every last part of your content. But that doesn’t mean it still isn’t something that search engines use.
By adding targeted, relevant keywords into your content, you let Google and other search engines know exactly what your page is about. During the indexing process, search engines pore over title tags, headers and body text to get clues as to how valuable a page is.
Properly optimizing for keywords shows them that your page is going to give users the information they want.
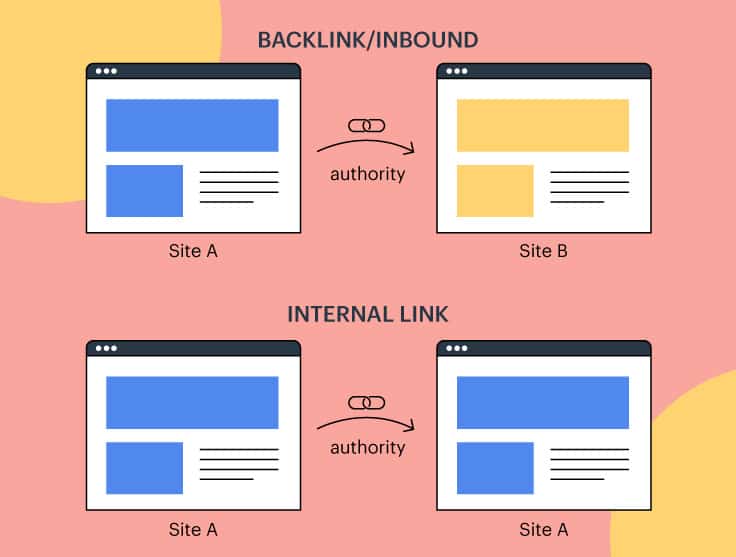
Authoritative Links
Although the importance of them has dropped since the early days of Google’s PageRank, high-quality backlinks are still a key part of search-engine rankings.
When a search-engine crawler sees a backlink to a page from a quality site, it treats it as a vote of confidence. Having lots of great links tells Google that a page has content worthy of getting such a valuable backlink. That’s the type of content Google wants users to find and will rank results accordingly.
On the other hand, a site with a lot of low-quality, spammy links built through private blog networks, comment spam and other paid tactics are a negative signal. Search engines — Google especially — have gotten better at sniffing out these black-hat SEO tactics. They will devalue a page’s link profile if it finds spammy links on it and, even worse, can impose a manual action penalty that can severely hurt a page’s rankings.
-
Expert Tip: Perform a proper backlink analysis to find any potentially harmful links. Evaluate them and determine whether it’s necessary to remove them.
Internal links also help search engines properly index and rank pages. Pages that are receiving links from other quality URLs on a site let them know that the page is important and related to them. Optimized internal linking can help strengthen how important and valuable pillar content is to a website, helping boost the rankings of a site’s most important pages.
Why It’s Crucial to Know How Search Engines Work
By knowing how search engines work, we can position our sites to give them the oomph they need to climb the rankings. What the algorithms aim to accomplish these days, ironically, is to focus less on what search engines want and more on what users are looking for.
After optimizing your robots.txt files, sitemaps and internal site structure to get your pages crawled and indexed, focus on making valuable, user-friendly content on every page. Search engines aim to find such pages for their users, so it’s the only way to rank well today.
Consider the most important ranking factors and make sure your site’s content surpasses the expectations of search engine algorithms. Find out what the search engines are rewarding for current SERPs and make your page better. Do that and you’ll start to see your page rankings move in the right direction.